Reviewed and edited by: Dr. William Sibuor, M.D. (BSc. Anat (Hons), MBChB)
Your immune system exists to fight dangerous things in your body, including mesothelioma tumors. Immunotherapy treatments can help your immune system work better. CTLA-4 inhibitors are immunotherapy drugs that can be used to treat mesothelioma and other diseases.
The goal of CTLA-4 inhibitors is to stop CTLA-4 from making it harder for you to fight mesothelioma. In other words, you have something inside you called CTLA-4 that slows down your immune system while it’s trying to kill mesothelioma tumor cells. That’s why this treatment aims to stop CTLA-4.
What CTLA-4 does in your immune system
CTLA-4 is like an auto-shutoff feature on appliances. Think about how your steam iron automatically turns off when the plate gets too hot or when it lies idle for a while. This is designed to avoid burning your clothes and causing serious accidents.
Your immune system is important because it helps protect you. But if it becomes too active, it can hurt you, causing autoimmune diseases. To keep your immune system from becoming too active, your body has natural immune checkpoints that lower your immune response. One immune checkpoint is CTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte Antigen 4).
CTLA-4 is an immune checkpoint protein that can be found on activated T-cells. T-cells fight dangerous things in your body like cancer cells, and they’re activated when their receptors attach to these dangerous cells. But CTLA-4’s job is to keep the T-cell from becoming too active, so it has a way to turn off the T-cell.
When CTLA-4 wants to turn a T-cell off, it moves from inside the T-cell to the surface. Then it displaces the dangerous cells from the normal receptors on the T-cells, and it binds to the receptors instead. Now that the T-cell isn’t attached to the dangerous cells anymore and is attached to CTLA-4 instead, the T-cell turns off (Sobhani et al, 2022).
Mesothelioma tumors are aggressive, and T-cells need to put up a strong fight. So, it doesn’t help when CTLA-4 turns T-cells off. CTLA-4 inhibitors are meant to solve this problem.
How CTLA-4 inhibitors work
Think about your iron again. Normally it’s good that it has an auto-shutoff feature. But if you’re ironing heavy pure cotton curtains with stubborn creases, you’ll need the iron to be continuously on and hot enough to get rid of the creases. There needs to be a way to override the auto-shutoff feature.
CTLA-4 inhibitors can do this in your immune system. CTLA-4 inhibitors are immunotherapy drugs that bind to and block the CTLA-4 protein on the surface of T-cells. This binding stops CTLA-4 from turning off T-cells. This way, the T-cells stay activated and can keep killing cancer cells.
Ipilimumab and tremelimumab are CTLA-4 inhibitors that are being studied as mesothelioma treatments (Thomas & Hassan, 2017). The figures below show how CTLA-4 inhibitors work to help your immune system fight cancer cells.

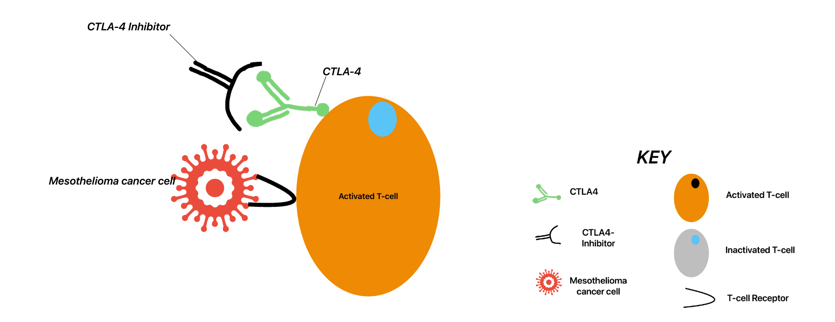
Effectiveness of CTLA-4 inhibitors against mesothelioma
There are several clinical trials studying CTLA-4 inhibitors to find out how well they work against mesothelioma. Sometimes CTLA-4 inhibitors are used alone, and other times they’re combined with another immunotherapy treatment like PD-1 inhibitors.
Some studies showed that CTLA-4 inhibitors helped people with mesothelioma live longer, but other studies showed that CTLA-4 inhibitors didn’t make a difference (Perrino et al, 2023). Right now, it’s hard to say one way or the other how effective CTLA-4 inhibitors are. The answers will become clearer as more clinical trials are done.
Side effects of CTLA-4 inhibitors
The side effects of CTLA-4 inhibitors usually involve the skin, liver, lungs, endocrine organs, and the gut. The most common side effects are diarrhea, colitis, skin rash, hepatitis and pneumonitis (Ji et al, 2019). These side effects are mostly autoimmune responses. Since CTLA-4, an immune checkpoint, is being inhibited, your immune system may get too active and start hurting normal cells. Talk with your healthcare provider about managing these symptoms.
Your T-cells are able to kill mesothelioma tumor cells. But CTLA-4’s job is to keep T-cells from becoming too active. To keep T-cells on and fighting at full strength, CTLA-4 inhibitor drugs stop CTLA-4 from turning off T-cells. This treatment may not work for everyone, but for some, it can help T-cells fight mesothelioma for longer.
References
- Sobhani N, Tardiel-Cyril D, Davtyan A, et al. CTLA-4 in Regulatory T Cells for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 2021; 13(6):1440
- Thomas, A., & Hassan, R. CTLA-4 blockade in mesothelioma: ineffective or reason for optimism?. The Lancet Oncology. 2021; 18(9):1150-51.
- Perrino M., De Vincenzo F., Cordua N., et al. Immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors and predictive biomarkers in malignant mesothelioma: Work still in progress. Frontiers in Immunology. 2023; 14: 1121557.
- Ji H, Tang X, Dong Z, et al. Adverse Event Profiles of Anti-CTLA-4 and Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibodies Alone or in Combination: Analysis of Spontaneous Reports Submitted to FAERS. Clin Drug Investig. 2019; 39(3):319-30.